Uncovering the causes of extreme phenomena (not just weather) using Rhenius entropy
Extreme events such as unusual weather patterns, financial market crashes or epileptic seizures are the subject of intensive research to understand their mechanisms and to develop early warning methods.
A new method, published in the prestigious scientific journal Science Advances [1], is helping to clarify which of several potential causes actually causes the extremes. The methodology was developed by colleagues at the Institute of Computer Science of the CAS (Milan Paluš, Pouya Manshour) and the Institute of Measurement of the Slovak Academy of Sciences (Martina Chvosteková). It uses Rényi entropy, an information measure that provides a deeper insight into complexity and variability in data.
The developed computational method has been tested on simulated and real climate data. It showed, for example, that for the extreme spring frosts in France that caused problems for grape growers, it is the Siberian pressure high that is responsible for the cold spring extremes, although the North Atlantic Oscillation and so-called blocking events (e.g. cyclones and anticyclones) also affect the temperature in France.
In addition to climate problems, the method is directly applicable to the study of causal relationships and the search for the sources of extreme events in many other areas.
The research was supported by the prestigious Academic Prize (Praemium Academiae) of the CAS, awarded to RNDr. Milan Paluš, DrSc.
Related projects: APVV-21-0216, VEGA č. 2/0023/22
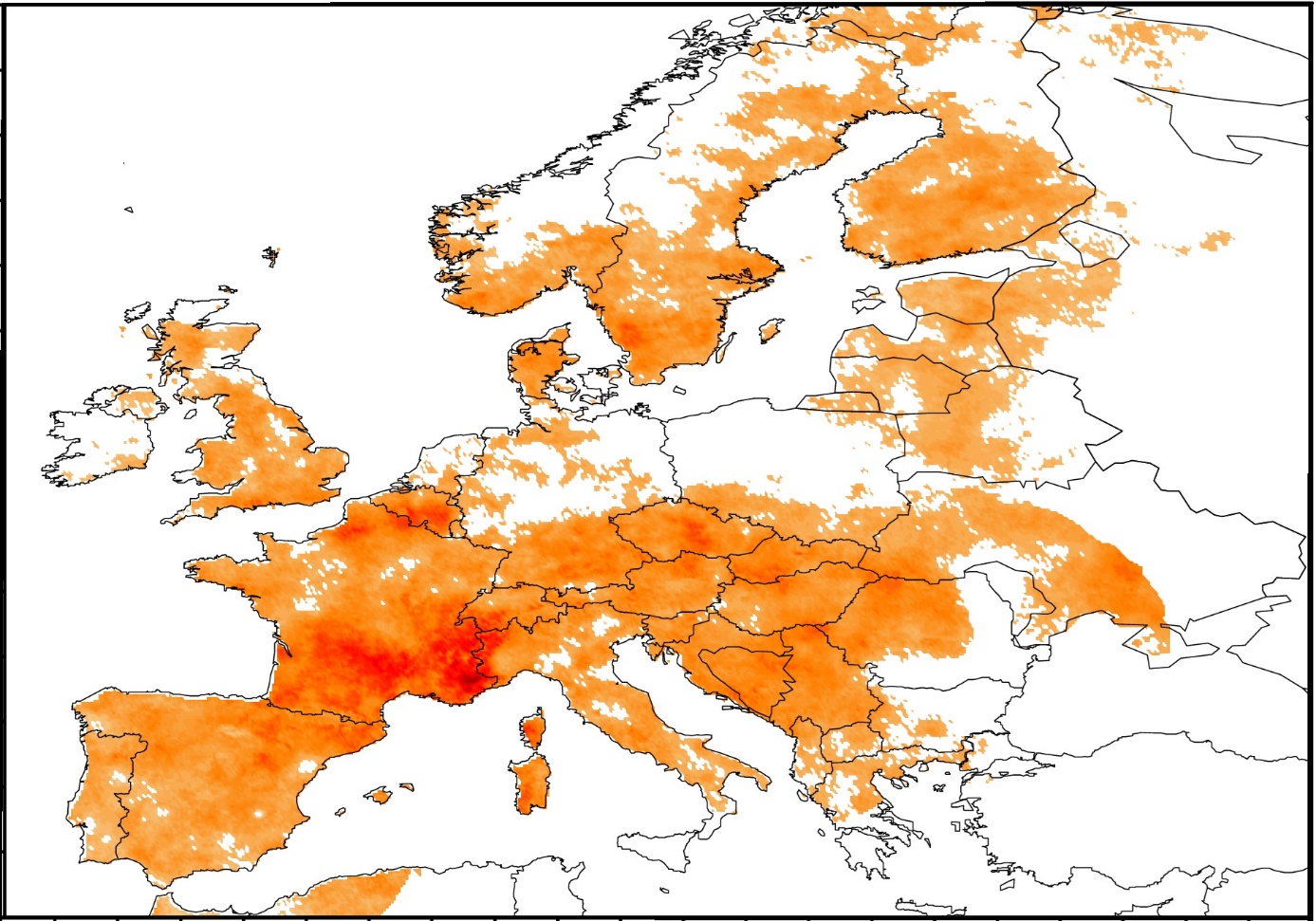
Fig.: Illustration of the coincidence analysis for cold extremes in spring air temperatures in Europe. Portions of cold extremes coincident with the SH condition (SH – Siberian High Pressure is the dominant circulation system over the Eurasian continent, formed by the massive accumulation of cold dry air in northeastern Eurasia from September to April). Only statistically significant agreement values (z-scores > 2) are highlighted in colour.
Publications:
- PALUŠ, M. – CHVOSTEKOVÁ, Martina– MANSHOUR, P. Causes of extreme events revealed by Rényi information transfer. In Science Advances, 2024, vol. 10, no. 30, art. no. 1721. (2023: 11.7 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 4.483 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 2375-2548. Dostupné na: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adn1721 Typ: ADCA
 Contacts
Contacts Intranet
Intranet SK
SK