Stress detection during scanning in an MRI tomography using continuous measurement of cardiovascular parameters using a photoplethysmographic optical sensor
Investigators: Přibil, Jiří, Přibilová Anna, Frollo, Ivan
Parallel measurement of cardiovascular parameters using a photoplethysmographic (PPG) optical sensor and standard portable blood pressure monitors was carried out in various situations of physical and mental stimulation and relaxation. The cardiovascular changes can be detected by the Oliva-Roztočil index values, the instant heart rate and the blood pressure. The proposed measurement procedure was tested in the preliminary experiments, various physiological and psychological stimuli ere applied to test whether the relaxation and activation phases produce different measured parameters suitable for further statistical analysis and processing. The picked-up PPG signal in the analog form was transferred to the external PC for digitalization and evaluation. The main experiment dealt with the analysis of vibration and acoustic noise influence on changes in the physiological and psychological state (stress factor) of a person lying inside the open MRI tomograph with a low magnetic induction value.
For enhancement of the measurement effectivity it will be necessary to construct a wearable PPG sensor with wireless data transfer capable of working in the environment of a weak magnetic field. The obtained results will be used for analysis, quantification, and suppression of the stress factor having an influence on the speech signal recorded during scanning in the MRI device for 3D modelling of a human vocal tract.
a) b) c)
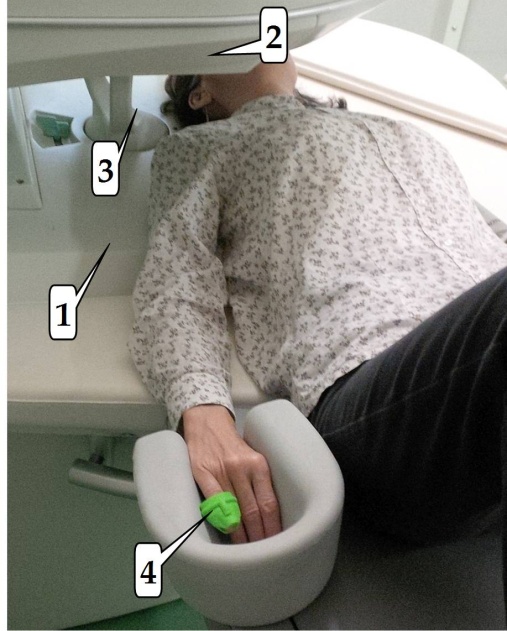
FIG. a): Documentation photo of measurement in the tomograph E-scan OPERA: (1)/(2) – upper/lower part of the gradient system, (3) center of the scanning space with the RF coil, (4) optical PPG sensor placed on a little finger of a right hand of a tested person.
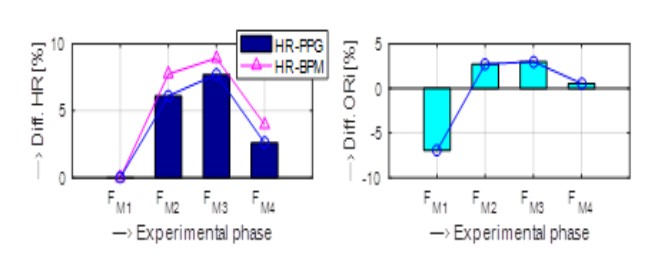
b) Graphical evaluation of heart rate (HR) values
c) Visualization of differential parameters of the Oliva-Roztočil index (ORi); phases of active MR scanning (FM2,3), initialization and relaxation phases (FM1 and FM4) of the measurement
Related projects:
- VEGA 2/0125/19 “Measurement and modeling of the electric field of the heart for non-invasive identification and interpretation of structural changes in the ventricular myocardium leading to ventricular arrhythmias”.
- COST Action CA16116 “Wearable robotic devices to enhance, support or replace human motor functions”.
- VEGA 2/0003/20 “Magnetic resonance imaging methods for medical diagnostics and materials research”.
Primary planned utilization in MR scanning of the human vocal tract with parallel recording of the speech signal during phonation is for medical purposes (e.g. observation of postoperative state of vocal cords), next for automatic conservation and reconstruction of the voice of patients after total laryngectomy (in cooperation with WBU Pilsen, Czech Republic). A potential applicator of the wearable PPG sensor with wireless data transfer can be also rescue teams in which it is necessary to monitor vital parameters in the conditions of severe physical and mental stress.
Publications:
- PŘIBIL, Jiří – PŘIBILOVÁ, Anna – FROLLO, Ivan. First-step PPG signal analysis for evaluation of stress induced during scanning in the open-air MRI device. In Sensors, 2020, vol. 20, no. 12, art. no. 3532. ISSN 1424-8220. (3.275-IF2019) Q1. Typ: ADCA
- PŘIBIL, Jiří – PŘIBILOVÁ, Anna – FROLLO, Ivan. Physiological impact of vibration and noise in an open-air magnetic resonance imager: Analysis of a PPG signal of an examined person. In Proceedings, 2020, vol. 42, no. 1, p. 1-14. ISSN 2504-3900. Typ: ADEB
 Contacts
Contacts Intranet
Intranet SK
SK