Method for measuring inorganic phosphate and intracellular pH in the healthy and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy hearts by in vivo cardiovascular magnetic resonance
Investigator: L. Valkovič
Failing heart is like a pump without fuel; where besides depletion in energy rich metabolites tissue often undergoes acidification. Measurement of intra-myocardial pH using typical magnetic resonance methods hindered by the dominant signal originating in blood that obscures inorganic phosphate (Pi) signal. We have therefore developed a new method using long repetition time and adiabatic excitation at ultra-high field system (7T), which allows, with 100% success rate, Pi detection and therefore pH calculation in human hearts. This method was demonstrated also in a small group of patients with hypertrophied cardiomyopathy, where it showed increased cardiac Pi concentration. This new method will provide answers for numerous clinically relevant questions related to the role of cardiac Pi and pH in cardiovascular and systemic disorders. We have also demonstrated high reproducibility of energy metabolism measurement using 7T MR. Described method will play a pivotal role in future research of cardiac metabolism.
Fig. 1 Fig. 2
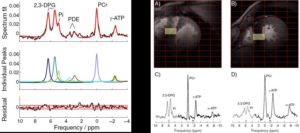
Fig. 1: A representative fit of a mid-septal spectrum measured during an even acquisition overlaid by the final spectral fit (top); individual peaks fitting (middle) and the residual (bottom) is depicted
Fig. 2: Representative mid-septal spectra with corresponding localizers acquired in a healthy subject (a, c) patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (b, d).
Related projects:
- VEGA 2/0001/17 – Measuring and imaging methods based on magnetic resonance for material and biomedical research
- APVV-15-0029 – Research of comparative imaging methods based on magnetic resonance for diagnostics of neurological and musculoskeletal diseases
Publications 2019:
- VALKOVIČ, Ladislav – CLARKE, W.T. – SCHMID, A.I. – RAMAN, B. – ELLIS, J. – WATKINS, H. – ROBSON, M.D. – NEUBAUER, S. – RODGERS, C.T. Measuring inorganic phosphate and intracellular pH in the healthy and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy hearts by in vivo 7T 31P-cardiovascular magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2019, vol. 21, p. 19. ISSN 1097-6647. (5.070-IF2018), Q1.
- ELLIS, J. – VALKOVIČ, Ladislav – PURVIS, L.A.B. – CLARKE, W.T. – RODGERS, C.T. Reproducibility of human cardiac phosphorus MRS (31P-MRS) at 7 T. In NMR in Biomedicine, 2019, vol. 32, no. 6, p. e4095. ISSN 0952-3480. (3.414-IF2018), Q1.
- PURVIS, L.A.B. – VALKOVIČ, Ladislav – ROBSON, M.D. – RODGERS, C.T. Feasibility of absolute quantification for 31P MRS at 7 T. In Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2019, vol. 82, no. 1, p. 49-61. ISSN 0740-3194. (3.858-IF2018), Q1.
- SEDIVY, P. – DEZORTOVA, M. – RYDLO, J. – DROBNY, M. – KRŠŠÁK, M. – VALKOVIČ, Ladislav – HAJEK, M. MR compatible ergometers for dynamic 31P MRS. In Journal of Applied Biomedicine, 2019, vol. 17, no. 2, p. 91-98. ISSN 1214-021X. (1.573-IF2018), Q2.
 Contacts
Contacts Intranet
Intranet SK
SK