Impact of the concentration of gadolinium-based macrocyclic contrast agents in human plasma on MRI signal strength at 1.5 T and 3.0 T and at different pulse sequences
Investigator: Pavol Szomolányi
Many factors provided by contrast media magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) influence is increasing in NMR signal strength. The effect on signal strength of different concentrations of gadolinium based contract agents and dilution of gadolinium-based macrocyclic contrast agents (GBCA) has been evaluated.
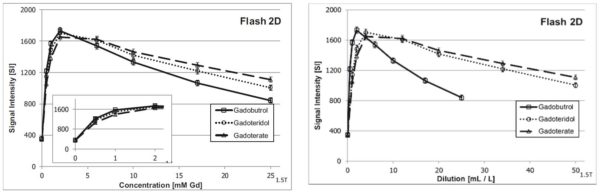
This phantom study examined gadobutrol, gadoteridol and gadoterate in human plasma of a healthy donor object at 37 °C. The different molar concentrations served to verify conditions that are usually relevant for steady-state imaging; dilutions were used to mimic the effect on the imaging of the bolus of the first-pass. Two magnetic scanners (Siemens) were used to measure signal strength. The samples were placed on a central slice of the tested vials. In a series of concentrations, gadobutrol showed the highest signal strength of all three GBCA, followed by gadoteridol and gadoterate. No major differences were observed between the 1.5 and 3T magnetic fields applied. In the dilution series, gadobutrol showed the highest signal strength of all three gadolinium-based contrast agents.
Fig. 1.: Signal intensities of three macrocyclic GBCAs at different concentrations and different dilutions at 1.5 T in plasma GBCA, gadolinium-based contrast agent.
Project: VEGA 2/0003/20 – Magnetic resonance imaging methods for medical diagnostics and materials research
Publications 2021:
- JURÁŠ, Vladimír – SZOMOLÁNYI, Pavol – SCHREINER, M.M. – UNTERBERGER, K. – KUREKOVA, A. – HAGER, B. – LAURENT, D. – REITHEL, E. – MEYER, H. – TRATTNIG, S. Reproducibility of an automated quantitative MRI assessment of low-grade knee articular cartilage lesions. In Cartilage, 2021. ISSN 1947-6035. (4.634 – F2020) Q1
- SZOMOLÁNYI, Pavol – FRENZEL, T. – NOEBAUER-HUHMANN, I.M. – ROHRER, M. – TRATTNIG, S. – PIETSCH, H. – ENDRIKAT, J. Impact of concentration and dilution of three macrocyclic gadolinium-based contrast agents on MRI signal intensity at 1.5T and 3T and different pulse sequences: Results of a phantom study in human plasma. In Acta Radiologica, 2020, vol. 62, no. 1, p. 51-57. ISSN 0284-1851. (1.990 – IF2020) Q2
- ZARIC, O. – JURÁŠ, Vladimír – SZOMOLÁNYI, P. – SCHREINER, M. – RAUDNER, M. – GIRAUDO, C. – TRATTNIG, S. Frontiers of sodium MRI revisited: From cartilage to brain imaging. In Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2020, vol. 54, no. 1, p. 58-75. ISSN 1053-1807. (3.954 – IF2019) Q1, D1
 Contacts
Contacts Intranet
Intranet SK
SK